Answers
Answer:
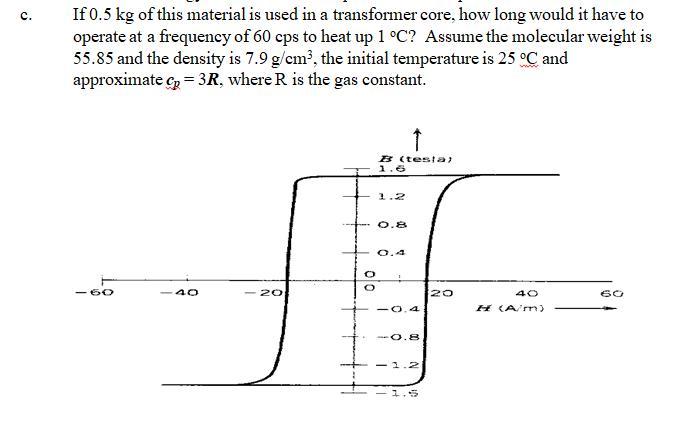
Hello your question is incomplete attached below is the complete question
answer : 49 seconds
Explanation:
considering only Hysteresis loss
we have to calculate the Area affected/under the Hysteresis loss
= volume * area
= 4 * ( 1.5 * 20 ) = 120 tesla. A/m
next we calculate the volume of the material
= mass of material / density
= 500 grams / 7.9 g/cm^3 = 6.33 * 10^-5 m^3
next we calculate the heat lost per cycle
= 6.33 * 10^-5 m^3 * 120 = 0.007596 joules
The total heat required to raise temperature by 1°c
= Cp * ΔT * n
= 3R * n * ΔT = 3(8.314) * 8.95 * 1 = 223.23 Joules
where n = number of moles = 500grams / 55.85 = 8.95moles
ΔT = 1
Therefore the time required to have to operate at a frequency of 60 cps
= Total heat required / heat lost per cycle
=( 223.23 / 0.007596 ) 60 cps
= 489.796 seconds ≈ 49 seconds
Related Questions
A child and sled with a combined mass of 53.9 kg slide down a frictionless slope. If the sled starts from rest and has a speed of 5.71 m/s at the bottom, what is the height of the hill
Answers
Answer:
1.66m
Explanation:
Using the conservation law
PE = KE
mgh = 1/2mv²
gh = V²/2
g is the acceleration due to gravity = 9.81m/s²
h is the height of the hill
V is the velocity = 5.71m/s
Substitute
9.81h = 5.71²/2
Cross multiply
2×9.81h = 5.71²
19.62h = 32.6041
h = 32.6041/19.62
h = 1.66m
Hence the height of the hill is 1.66m
how are s waves and p waves simuliar?
A.they shake the ground
B.they travel through liquids
C. they arrive at the same time
D.they shake the ground from side to side
Answers
Answer:
A
Explanation:
hope this helps
A car is stopped for a traffic signal. When the light turns green, the car accelerates, increasing its speed from zero to 7.63 m/s in 3.94 s. What is the magnitude of the linear impulse experienced by a 73.7 kg passenger in the car during this time? Submit Answer Tries 0/20 What is the average force experienced by the passenger?
Answers
Answer:
1. p = 562.3 kg*m/s
2. F = 142.7 N
Explanation:
1. The linear impulse (p) is given by:
[tex] p = mv [/tex]
Where:
m: is the passenger's mass = 73.7 kg
v: is the speed = 7.63 m/s
[tex] p = mv = 73.7 kg*7.63 m/s = 562.3 kg*m/s [/tex]
Hence, the magnitude of the linear impulse experienced by a passenger is 562.3 kg*m/s.
2. The average force can be calculated using the following equation:
[tex] F = \frac{m(v_{f} - v_{0})}{t} = \frac{73.7 kg(7.63 m/s - 0)}{3.94 s} = 142.7 N [/tex]
Therefore, the average force experienced by the passenger is 142.7 N.
I hope it helps you!
An object is accelerating if it is moving?
Answers
9514 1404 393
Answer:
Not Necessarily
Explanation:
If the object is changing speed or direction, then it is accelerating. If it is maintaining the same speed and direction, it is not accelerating.
A diffusion couple, made by welding a thin onecentimeter square slab of pure metal A to a similar slab of pure metal B, was given a diffusion anneal at an elevated temperature and then cooled to room temperature. On chemically analyzing successive layers of the specimen, cut parallel to the weld interface, it was observed that, at one position, over a distance of 5000 nm, the atom fraction of metal A, NA, changed from 0.30 to 0.35. Assume that the number of atoms per m3 of both pure metals is 9 x 10^28. First determine the concentration gradient dnA/dx. Then if the diffusion coefficient, at the point in question and annealing temperature, was 2 10^-14 m^2/s.
Required:
Determine the number of A atoms per second that would pass through this cross-section at the annealing temperature.
Answers
Answer:
The value is [tex]H = 18*10^{2} \ Atom / sec [/tex]
Explanation:
From the question we are told that
The atom fraction of metal A at point G is [tex] A = 0.30 \ m[/tex]
The atom fraction of metal A at a distance 5000nm from G is [tex]A_2 = 0.35[/tex]
The number of atoms per [tex]m^3[/tex] is [tex]N_h = 9 * 10^{28}[/tex]
The diffusion coefficient is [tex]D = 2* 10^{-14 } m^2/s[/tex]
Generally of the concentration of atoms of metal A at G is
[tex] N_A = A * N_h [/tex]
=> [tex] N_A = 0.3 * 9 * 10^{28}[/tex]
=> [tex] N_A = 2.7 * 10^{28} 2.7 atoms/m^3[/tex]
Generally of the concentration of atoms of metal A at a distance 5000nm from G is
[tex]D = 0.35 *9 * 10^{28}[/tex]
=> [tex]D = 3.15 * 10^{28} \ atoms / m^3[/tex]
The concentration gradient is mathematically represented as
[tex]\frac{dN_A}{dx} = \frac{(3.15 - 2.7) * 10^{28} }{5000nm - 0 }[/tex]
=> [tex]\frac{dN_A}{dx} = \frac{(3.15 - 2.7) * 10^{28} }{[5000 *10^{-9}] - 0 }[/tex]
=> [tex]\frac{dN_A}{dx} = 9 * 10^{20} / m^4[/tex]
Generally the flux of the atoms per unit area according to Fick's Law is mathematically represented as
[tex]J = -D* \frac{d N_A}{dx}[/tex]
=> [tex]J = -2* 10^{-14 * 9 * 10^{20} [/tex]
=> [tex] J = 18*10^{6}\ atoms\ crossing\ /m^2 s [/tex]
Generally if the cross-section area is [tex] a = 1 cm^2 = 10^{-4} \ m^2[/tex]
Generally the number of atom crossing the above area per second is mathematically is
[tex]H = 18*10^{6} * 10^{-4} [/tex]
=> [tex]H = 18*10^{2} \ Atom / sec [/tex]
anyone to assist me on it ...especial page7 and 8
Answers
Answer:
i needed points it was an emergency sorry
Explanation:
If vector A = 6i - 2j + 3k, determine
(a) A vector in the same direction as A with magnitude 2A
(b) A unit vector in the direction of A
(c) a vector opposite to A with magnitude of 4 m
Answers
Answer:
(a) [tex]2\vec A=12\hat i-4\hat j+6\hat k[/tex]
(b) [tex]\displaystyle \vec{U_A}=12/7\hat i-4/7\hat j+6/7\hat k[/tex]
(c) [tex]-4\vec{U_A}=-48/7\hat i+16/7\hat j-24/7\hat k[/tex]
Explanation:
Vectors
Given a vector
[tex]\vec A=6\hat i-2\hat j+3\hat k[/tex]
We must determine the following:
a) A vector in the same direction as A with double magnitude 2A.
If the vector goes in the same direction but has a different magnitude, we only need to multiply each component by a common factor, in this case, by 2. Thus, the required vector is:
[tex]2\vec A=12\hat i-4\hat j+6\hat k[/tex]
b) A unit vector in the same direction of A.
The unit vector needs to compute the magnitude of the vector:
[tex]\mid A\mid=\sqrt{6^2+2^2+3^2}[/tex]
[tex]\mid A\mid=\sqrt{36+4+9}=\sqrt{49}=7[/tex]
[tex]\mid A\mid=7[/tex]
The unit vector is:
[tex]\displaystyle \vec{U_A}=\frac{\vec A}{\mid \vec A\mid}[/tex]
[tex]\displaystyle \vec{U_A}=\frac{12\hat i-4\hat j+6\hat k}{7}[/tex]
[tex]\displaystyle \vec{U_A}=12/7\hat i-4/7\hat j+6/7\hat k[/tex]
c) A vector opposite to A with magnitude 4 m. We assume the original vector is also expressed in m.
The opposite vector to A is obtained simply by multiplying the unit vector by -1. To make its magnitude equal to 4, also multiply by 4. In all, we multiply the unit vector by -4:
[tex]-4\vec{U_A}=-4(12/7\hat i-4/7\hat j+6/7\hat k)[/tex]
[tex]-4\vec{U_A}=-48/7\hat i+16/7\hat j-24/7\hat k[/tex]
A metal ball sits motionless on a flat surface. Which of these would make the ball move?
A. The force of gravity becomes less.
B. The force of gravity becomes greater.
C. Two equal horizontal opposing forces act upon the ball.
D. Two unequal horizontal opposing forces act upon the ball.
Answers
Answer:
D
Explanation:
Unbalanced forces move stuff. Gravity would only increase/decrease movement if the object was already in motion.
Answer:
b
Explanation:
In which medium does the light move faster, water or diamond?
Answers
1. What is the chemical name of the following chemical symbols?
Be
Nel
Mg
Na
Answers
Answer:
Na sodium
Mg magnesium
Be beryllium
Explanation:
Nel is not any element it is wrong
which equation should be used to find speed
Answers
Answer:
The formula for speed is speed = distance ÷ time. To work out what the units are for speed, you need to know the units for distance and time. In this example, distance is in metres (m) and time is in seconds (s), so the units will be in metres per second (m/s).
The coefficient of static friction between m1 and the horizontal surface is 0.50, and the coefficient of kinetic friction is 0.30. (a) If the system is released from rest, what will its acceleration be
Answers
This question is incomplete
Complete Question
m1 is 10kg, m2 is 4.0kg. The coefficient of static friction between m1 and the horizontal surface is 0.50. and the Coefficient of kinetic friction is 0.30.
a) if the system is released from rest what will be its acceleration
Answer:
0.7 m/s²
Explanation:
The coefficient of static friction between m1 and the horizontal surface is 0.50. and the coefficient of kinetic friction is 0.30.
(a) if the system is released from rest what will be its acceleration
g = acceleration due to gravity = 9.81 m/s²
Coefficient of Kinetic Friction = μk = 0.30
m1 = 10kg
m2 = 4.0kg
The formula to solve question a is given as:
a = acceleration at rest
m2g- μk m1g = (m1+ m2) a
Making a the subject of the formula:
a = (m2g- μk×m1g )/(m1+ m2)
a = [(4.0 kg × 9.81m/s²) – (0.30 ×9.81 × 10) ]/(10+4)
a = 0.7 m/s²
Find the angle between the two unitless vectors: F1 = 8.92 i + 17.37 j F2 = 12.44 i + 7.11 j Answer in degrees, and to the fourth decimal place.
Answers
Answer:
θ = 33.0705°
Explanation:
The angle between the two vectors is given by the formula;
Cos θ = (F1 • F2)/(|F1| × |F2|)
We are given;
F1 = 8.92i + 17.37j
F2 = 12.44i + 7.11j
Thus;
Cos θ = [(8.92i + 17.37j) • (12.44i + 7.11j)]/[√(8.92² + 17.37²) × √(12.44² + 7.11²)]
Cos θ = (110.9648 + 123.5007)/(19.5265 × 14.3285)
Cos θ = 0.8380
θ = cos^(-1) 0.8380
θ = 33.0705°
gold has a density of 19.32g/cm3. if you have a 25 cm3 sample of gold what is the mass of the sample
Answers
Answer:
ggggggggggggggggggggggggggggg
Explanation:
Answer:
The volume of the sample of gold is
16.51 [tex]cm^{3}[/tex]
Explanation:
The formula for density is:
D= [tex]\frac{M}{V}[/tex].
where:
D is density,
M is mass, and
V is volume.
Rearrange the density formula to isolate volume.
V= [tex]\frac{M}{D}[/tex]
V= [tex]\frac{318.97g Au}{19.32g cm^{3}}[/tex]
V= 318.97∅ × [tex]\frac{1 cm^{3} Au}{19.32g cm^{3} }[/tex]← Multiply by the multiplicative inverse of the density.
V= 16.51 cm³ Au.
1
2
3
4
5
6
8
9
10
Dressing appropriately for exercise includes
A. wearing the same clothes for all exercises
B. choosing dark colored clothing when exercising at night
C. wearing sunscreen when exercising outside
D. making sure you wear the best brand-name clothes
Please select the best answer from the choices provided.
A
B.
C.
D.
The answer is C.
Answers
Answer:
the answer is C
Explanation:
you said its c
The volume of water in a water bottle, is about 398
g
cm
km/hr
Kg
g/mL
ml
km
m/s
Answers
Answer:
milliliters (ml)
Explanation:
millileters is the correct measurement for liquids
If a rock is skipped into a lake at 24 m/s2, with that what force was the rock thrown if it was 1.75kg?
Answers
Answer: f= M×A
1.75kg×24= 42N
Explanation:
Because to find force you do Mass times acceleration so I did 1.75 kg times 24 would equal 42 Newtons!
1. What is Ohm"s law?
2. If you placed a negatively charged hairbrush near your hair, what charge would your hair be?
3. You must change a lightbulb and the new lightbulb has a larger resistance. If the voltage of the battery does not change, what happens to the current going through the flashlight?
HELLPPPP
Answers
1. Ohm's law shows the relationship between:
voltagecurrentresistanceFormula: voltage = current x resistance
2. The negative charge on the hairbrush will induce a positive charge on your hair. As a result, your hair is going to be attracted to the hairbrush (and repelled by other strands of hair.)
3. V = IR, so if the resistance of the current increases, and the voltage of the current stays the same, there is as a result, going to be less current.
Best of Regards!
if you are driving 110 km/h along a straight road and you look to the side for 2.0 s , how far do you travel during this inattentive period ? explain.
Answers
Explanation:
hope this helps, have a good one :D
Answer:
60.12m
Explanation:
Distance = Velocity x Time
To use this formula we must first convert 110km/h to m/s, which we can do by dividing the value by 3.6:
110/3.6 = 30.56m/s (2dp)
Velocity = 30.56m/s
Time = 2s
Distance = 30.56x2
Distance = 61.12m
You travel 60.12m during this inattentive period.
Hope this helped!
At time t = 0 the point at x = 0 has velocity v0 and displacement y0. The phase constant φ is given by tanφ =:
Answers
This question is incomplete, the complete question is;
The displacement of a string carrying a traveling sinusoidal wave is given by y(x,t)=ymsin(kx - ωt -φ) .
At time t = 0, the point at x = 0 has velocity v₀ and displacement y₀.
The phase constant φ is given by tanφ =:
A) ωv₀ /y₀
B) ωv₀ y₀
C) v₀ /ωy₀
D) y₀ /ωv₀
E) ωy₀ /v₀
Answer:
E) ωy₀ /v₀
Explanation:
Given that;
displacement of a wave is; y(x,t) = ym sin (kx - ωt - φ)
we differentiate the given equation with respect to time
d/dt (y(x,t)) = d/dt(ym sin(kx - ωt - φ) )
v(0,0)) = -ym ωcos (k(0) - ω(0) - φ) )
v₀ = -ym ωcos (-φ) ......... lets leave thisas equ 1
At t = 0, x = 0
the displacement of the wave is
y(0,0) = ym sin (k(0) - ω(0) - φ)
y₀ = ym sin(-φ) ..............let this be equ 2
y₀/v₀ = (ym sin(-φ)) / (-ym ωcos (-φ)) = ( -ym sin(φ)) / (-ym ωcos (φ))
(tanφ)/ω = y₀/v₀
tanφ = y₀ω/v₀
therefore the required value is y₀ω/v₀
option (E).
A 10-ohm resistor has a constant current. If 1200 C of charge flow through it in 4 minutes what
is the value of the current?
A. 3.0 A
B 5.0 A
C. 11 A
D. 15 A
E. 20A
Answers
Answer:
B 5.0 A .
Explanation:
Hello.
In this case, since we know the charge (1200 C), time (4 min =240 s) and resistance (10Ω) which is actually not needed here, we compute the current as follows:
[tex]I=\frac{Q}{t}[/tex]
Then, for the given data, we obtain:
[tex]I=\frac{1200C}{4min}*\frac{1min}{60s}\\\\I=5A[/tex]
Therefore, answer is B 5.0 A .
Best regards!
3 For this force system the equivalent system at P is ___________ A FRP 40 lb along x dir and MRP 60 ft lbB FRP 0 lb and MRP 30 ft lbC FRP 30 lb along y dir and MRP 30 ft lbS FRP 40 lb along x dir and MRP 30 ft lb
Answers
This question is incomplete, the complete question is;
For this force system the equivalent system at P is ___________
A) FRP = 40 lb (along +x-dir.) and MRP = +60 ft.lb
B) FRP = 0 lb and MRP = +30 ft.lb
C) FRP 30 lb (along +y-dir.) and MRP = -30 ft.lb
D) FRP 40 lb (along +x-dir.) and MRP = +30 ft.lb
Answer:
D) FRP 40 lb (along +x-dir.) and MRP = +30 ft.lb
Explanation:
From the figure in the image i uploaded along this answer;
FRP = ( 40 lb i + 30 lb j ) + [30 lb (-j)]
Where i and j are the unit vectors along X & Y axis respectively.
So, FRP = 40 lb i
that is, FRP = 40 lb along +X direction
MRP = [ 30 lb x ( 1 ' + 1' ) ] +( -30 lb x 1 ' )
= (30 lb x 2 ' )- 30 lb ft
= 60 lb ft - 30 lb ft
= 30 lb ft
Therefore option(D) is correct
A charged isolated metal sphere of diameter 12 cm has a potential of 9200 V relative to V = 0 at infinity. Calculate the energy density in the electric field near the surface of the sphere.
Answers
Answer:
0.1 J/m³
Explanation:
We know that
V = k Q / R
We also know that
E = k Q / R²
Joining the two equations together, we have
E = V / R
To solve the question proper, we'd be using the formula
u = 1/2 E• E², substitute for E, we have
u = 1/2 E• (V/R)²
u = 1/2 * 8.85*10^-12 * (9000 / 0.06)²
u = 1/2 * 8.85*10^-12 * 150000²
u = 1/2 * 8.85*10^-12 * 2.25*10^10
u = 1/2 * 0.199125
u = 0.0996
u = 0.1 J/m³
The energy density is 0.1 J/m³
I WILL GIVE BRAINLIEST
In which of the following locations would most likely find parenchyma cells? Leaves roots flowers bark
Answers
Answer:
I would guess its leaves
Answer:
Leaves
Explanation:
21. A toy car starts from rest and begins to accelerate at 11.0 m/s2. What is the toy
car's final velocity after 6.0 seconds?
Answers
Answer:
Explanation:
Given parameters:
Initial velocity = 0
Acceleration = 11m/s²
Time = 6s
Unknown:
Final velocity = ?
Solution:
From the given parameters, we use one of the appropriate equations of motion to solve this problem.
V = U + at
V is the final velocity
U is the initial velocity
a is the acceleration due to gravity
t is the time taken
Input the parameters and solve;
V = 0 + 11 x6
V = 66m/s
The final velocity is 66m/s
calculating light in physics
Answers
c = the speed of light = 300,000 km/s or 3.0 x 108 m/s.
= the wavelength of light, usually measured in meters or Ångströms (1 Å = 10-10 m)
f = the frequency at which light waves pass by, measured in units of per seconds (1/s).
what happens to the temperature of water as time elapses? IF YOU ANSWER IT I WILL MARK YOU A BRAINLEST ANSWER
Answers
Answer:
I think it will get colder
Explanation:
Answer:
The water molecules go faster as it gets colder they go slower
Explanation:
trust me thats the answer
Please provide explanation!!!
Thank you.
Answers
Answer:
(a) 102 cm/s
(b) 0.490 cm²
Explanation:
(a) Use Bernoulli equation.
P₁ + ½ ρ v₁² + ρgh₁ = P₂ + ½ ρ v₂² + ρgh₂
0 + ½ ρ v₁² + ρgh₁ = 0 + ½ ρ v₂² + 0
½ ρ v₁² + ρgh₁ = ½ ρ v₂²
½ v₁² + gh₁ = ½ v₂²
½ (25.0 cm/s)² + (980 cm/s²) (5.00 cm) = ½ v²
v = 102 cm/s
(b) The flow rate is constant.
v₁ A₁ = v₂ A₂
(25.0 cm/s) (2.00 cm²) = (102 cm/s) A
A = 0.490 cm²
Plates slide past one another at____.
A. Subduction zones
B. Transform boundaries
C. Convection currents
D. Divergent boundaries
Answers
Answer:
Transform Boundary
Explanation:
The just slide past each other
Answer:
Transform Boundaries
Explanation:
The power that a student generates when walking at a steady pace of vw is the same as when the student is riding a bike at vb = 3vw. The student is going to travel a distance d. The energy the student uses when walking is Ew. The energy the student uses when biking is Eb. The ratio EwEb is
Answers
Answer:
3
Explanation: